I.Swift Economic Development
Before the founding of New China in 1949, Xinjiang had a natural economy mainly comprised of farming and animal husbandry. Local development was stagnant, with low productivity levels and underdeveloped production modes. There was not an inch of railway, no large-scale farms or large fertile fields. Privately owned small workshops were what signified industry here. The people led a life of poverty and hardship.
Since 1949, particularly after China's reform and opening-up in the late 1970s, Xinjiang has entered an era of rapid economic and social progress and enhanced comprehensive strength, with the local residents enjoying the most tangible benefits. Proceeding from the state development strategy and the fundamental interests of the people of various ethnic groups, the Chinese government has paid great attention to the development and construction of Xinjiang. It has made it a national basic policy to help the frontier areas develop their economy for the common good and wealth, and worked out timely a series of strategic decisions to promote Xinjiang's development. Xinjiang has been given priority in the national strategy launched in 2000 to develop the western regions.
Over the years, Xinjiang has made full use of its own advantages, and focused on economic restructuring and changing the modes of economic growth, infrastructure construction and environmental protection, along with improvement of people's livelihood and basic public services, so as to keep the development of Xinjiang in pace with the national development, and to ensure beneficial interaction between the development of southern Xinjiang and that of northern Xinjiang.
— Comprehensive strength remarkably enhanced. Calculated at constant prices, the local GDP in 2008 stood at 420.3 billion yuan, which is 86.4 times higher than that of 1952 (three years before the establishment of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region), up 8.3% on average annually; 19.6 times over that of 1978 (the first year of reform and opening-up), up 10.4% on average annually; and 2.2 times above that of 2000 (launching of the western development campaign), up 10.6% on average annually. Local revenues reached 36.106 billion yuan in 2008, which is 4.56 times that of 2000, 50.57 times that of 1978, and 208.71 times that of 1955.
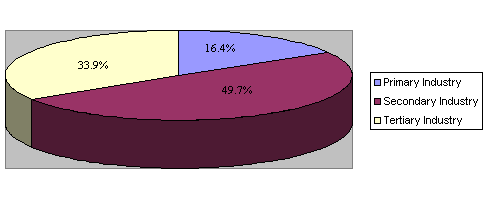
— Economic structure gradually optimized. In recent years, Xinjiang has witnessed rapid growth of its industry, agriculture, and service sector. As industrialization quickens, industry has replaced agriculture to become the pillar economic sector. Tertiary industry, or services, is also playing a prominent role in economic advancement. Wholesale and retail businesses and catering industry have expanded swiftly, while post and telecommunications networks have been widely set up, and new sectors, such as real estate and finance, are booming. In 2008, primary, secondary and tertiary industries accounted for, respectively, 16.4%, 49.7% and 33.9% of the local GDP.
Fig.1 Xinjiang's Industrial Structure
— Infrastructure construction reinforced. Given its "irrigation farming in oases,"Xinjiang has built a number of large modern water conservancy projects, such as the Kizil Reservoir in Aksu and the Ulug Ata Reservoir in Hotan, in addition to canals, ditches and seepage control projects, which have greatly increased the amount of water diverted, reservoir storage capacity and effectively irrigated areas. The completion of the Tarim River improvement project in 2008, with an investment of more than 10 billion yuan, put an end to the river's 30-year history of running dry for some 300 km in its lower reaches. Efforts in building shelterbelts of north, northeast and northwest China, greening the plain areas, returning farmlands to forests and returning pastures to grasslands have also improved farming conditions. Drip and spray irrigation is now available to nearly 800,000 ha of farmlands, thus saving five billion cubic meters of water annually.
By the end of 2008, Xinjiang had completed eight national highways, 66 inter-province highways, and more than 600 county-level roads, with the combined mileage reaching 147,000 km. A highway network has taken shape centering on Urumqi (capital city of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region), with roads surrounding the two basins (Junggar and Tarim) and crossing the two large deserts (Gurbantunggut and Taklimakan) and the Tianshan Mountains, to link southern and northern Xinjiang. With the completion of railways going through southern and northern Xinjiang and the Lanzhou-Xinjiang double-track rails, the total length of railroads in Xinjiang surpassed 3,000 km by 2008. Civil aviation has expanded swiftly, and a network with 114 domestic and international flight routes has formed, radiating from Urumqi and connecting some 70 Chinese and foreign cities and 12 prefectures in Xinjiang, with flight routes totaling over 160,000 km. Xinjiang now boasts the largest number of airports and the longest flight routes among all provinces and autonomous regions in China.
The post and telecommunications industry has seen rapid growth. A complete modern communications system has been put in place, composed of program-controlled exchanges, fiber-optical communication, digital microwave, as well as satellite and mobile communications; and the entire region has been covered by optical cable, digital microwave and satellite communications.
— Overall agricultural production capacity notably enhanced. Xinjiang boasts abundant agricultural resources. In recent years, the industrialized production of grain, cotton, special fruit and quality livestock farming as well as agriculture facility building have quickened, and industrialized belts of advantageous and special farming products are taking shape. The fundamental status and overall production capacity of agriculture have both been enhanced, and the effective supply of agricultural products is increasing multifold.
In 2008, agricultural added value reached 69.1 billion yuan, 1.4 times more than that of 2000; and the total output of grain was 10.2285 million tons, leaving a slight surplus after meeting local demand. As one of China's major bases of commercial cotton, Xinjiang produced 3.0155 million tons of cotton in 2008, ranking first in China in terms of total output, per-unit output and per-capita output.
Modern animal husbandry has accelerated its growth, and it now accounts for 27% of local agricultural output value. In 2008, meat output stood at 1.7549 million tons, up 95% from 2000. Fruit production is also increasing quickly. In 2008, the total area of fruit trees exceeded one million ha, and fruit output totaled over four million tons, worth six billion yuan in output value.
By 2008, Xinjiang had 1,059 enterprises engaged in agricultural produce processing. It is the largest tomato processing and export base in China. Its daily dairy-processing capacity has been boosted from less than 1,000 tons to nearly 3,000 tons in a couple of years, the fastest growth in all provinces and autonomous regions. It is also the largest production base of beet sugar in China, with an annual output of 600,000 tons. The wine-making industry is advancing dynamically. Agricultural processing has made production-on-order available to more than half of the planting areas, benefiting 65% of rural households.
— Modern industry system gradually formed. Xinjiang's industry has grown out of nothing, and developed from small to big. In recent years, through transforming advantageous resources, and supporting large enterprises and groups while nurturing small and medium-sized ones, Xinjiang has quickened its industrialization pace. Its main industrial products have seen multiple increases in output; and a complete modern industrial system has taken shape, comprising petroleum, coal, iron and steel, chemical industries, power, building materials, and textiles. Industrial zones have emerged, including the economic belt on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains, the Urumqi-Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture integrated economic zone and the Korla-Kuqa petrochemical belt, while 32 national and regional industrial parks have been built.
Industry has become an important factor propelling the local economy. In 2008, the industrial sector reported a 52.3% contribution to local economic growth, and industrial added value totaled 179.07 billion yuan, 274 times more than that of 1952, 16.6 times above 1978, and 3.98 times more than figures in 2000. The use of information technology in major industries and sectors has been strengthened, while the total amount of major pollutants discharged has been basically controlled, and energy-saving and emission-reduction efforts have yielded good results.
— Mineral resources further developed. Xinjiang is one of Chinese regions rich in oil, gas and coal resources. Encouraged by the state policy of large-scale exploration and development through big investments, Xinjiang has endeavored to turn its resource advantages into economic advantages, and to boost the local economy through resources development so as to benefit all people in Xinjiang.
In 2008, Xinjiang ranked second in China by generating 27.22 million tons of crude oil; and first, by producing 24 billion cubic meters of natural gas. Driven by local oil-and-gas development and China's co-operation with West Asian countries in relevant fields, the construction of pipelines in Xinjiang is advancing rapidly. By 2008, Xinjiang had a network of pipelines whose total length exceeded 4,000 km, covering southern, northern and eastern Xinjiang.
In recent years, thermal power and coal-chemical industries have boomed in Xinjiang. The rapid growth of energy and chemical industries has not only met local demands for energy and petrochemical products, but also spurred services and other relevant sectors. This is important for the formation and upgrading of regional economic structure, as well as for job creation and the urbanization rate.
— Opening wider to the world. Xinjiang is one of China's major gateways opening to the west. It is also an important passageway on the new Eurasian continental bridge. Bordered by Mongolia, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan and India, Xinjiang has the longest land borders among all frontier provinces and autonomous regions in China. Since China's reform and opening-up in 1978, Xinjiang has experienced a change from being closed or semi-closed to all-round opening up.
Now, Xinjiang has 17 Grade-I ports approved by the state and 12 Grade-II ports approved by the autonomous region itself, linking it immediately to over a dozen surrounding countries. By the end of 2008, Xinjiang was conducting economic and trade cooperation, as well as scientific and technological and cultural exchanges, with 167 countries and regions.
In 2008, Xinjiang's volume of foreign trade reached US$22.217 billion, ranking 12th in China (and second among central and western municipalities, provinces and autonomous regions); it made US$164 million in non-finance direct investment abroad, ranking 13th in China; and its turnover from overseas contracted projects reached US$795 million, ranking 14th. The region dispatched 8,548 people to work overseas, ranking 13th in China.
— Tourism has witnessed buoyant growth. In recent years, Xinjiang's tourism has become a new economic growth point. By 2008, the region has opened nearly 500 scenic zones or spots. Besides the main tourist route along the Silk Road, there are also the Kanas Lake ecotourism zone, the Heavenly Lake, Sayram and Bosten lakes, ancient cultural ruins in Turpan and Kuqa, the folk customs zone in Kashi (Kashgar), and the Ili grasslands. In 2008, Xinjiang hosted 22.3132 million foreign and domestic visitors, and reported nearly 20 billion yuan in tourism revenues.
— Regional economic growth coordinated. The state and the autonomous region have supported areas with advantageous conditions to take the development lead, while adopting preferential policies and measures to boost the development of southern Xinjiang (with the focus on Kashi, Hotan and Kizilsu Kirgiz Autonomous Prefecture) as well as pastureland and frontier areas, for more balanced development between southern and northern Xinjiang, and between urban and rural areas.
The economic belt on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains will take the initiative in taking on the industries from China's eastern coast, so as to build a new industrial base. Urumqi-Changji integration will be accelerated, while construction of national export processing zones, development zones and industrial parks will be sped up, and a modern service sector will be further developed. Based on oil and gas resources, and thermal power and coal-chemical industries, the construction of the Turpan-Hami petrochemical belt on the southern slope of the Tianshan Mountains will be expedited to seek a congregating effect of large projects to form groups of ancillary industries.
Great efforts will be made to promote the economic and social development of the three prefectures (i.e., Kashi, Hotan and Kizilsu Kirgiz Autonomous Prefecture) in southern Xinjiang, with priorities on a number of projects that are central to long-term development and improvement of people's livelihood, such as quakeproof housing, transformation of the old town of Kashi, rural infrastructure construction, underground water tapping, reclamation of salinealkali lands, provision of safe drinking water, and spread of biogas in the countryside. Preferential policies shall be adopted to improve production and living conditions in pastureland and frontier areas, and to accelerate their development.
The great economic achievements are the results of concerted efforts by all peoples of Xinjiang, and of support from the central government and the entire nation. Over the years, the central government has, in formulating plans on national economic and social development, listed Xinjiang's projects in infrastructure, agricultural development and a modern industrial system construction as key state projects enjoying preferential policies and funding support.
From 1950 to 2008, the central government invested 386.23 billion yuan in Xinjiang, accounting for 25.7% of the total investment in the region. From 1955 (when the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region was established) to 2008, Xinjiang received a total of 375.202 billion yuan in subsidies from the central budget. Along with the implementation of the western region development campaign in 2000, the amount of subsidies has grown by 24.4% on average annually, reaching 68.56 billion yuan in 2008. The central government has increased capital input and support to the region by using loans from international financial organizations and foreign governments.
In recent years, to optimize Xinjiang's industrial structure, the central government has moved a number of enterprises and factories from the economically more developed southeast coast to Xinjiang, and transferred engineers and technicians from other areas to the region's newly built pillar enterprises. A large number of workers from Xinjiang's ethnic minorities have been selected to work as interns in other areas, thus fostering a contingent of skilled workers for the region within a short period.
Moreover, the various municipalities and provinces have been paired up with different parts of Xinjiang to provide the latter with large sums of capital, technology and talent, which have played an important role in the region's development. On the one hand, the more-developed areas have dispatched technicians, teachers, doctors, management personnel and other professionals to work in Xinjiang's prefectures and counties, to disseminate advanced technology and concepts. On the other, Xinjiang has dispatched teams of its own officials, technicians and workers from Party and government organs, as well as economic management departments, to work and study in relevant provinces and municipalities.
In recent years, at the request of the central government, Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, Zhejiang, Shandong, Liaoning, Jiangxi and Henan as well as 15 state-owned large enterprises have been paired up with 33 counties (or cities) in southern Xinjiang to provide them with economic, scientific and technological, and cultural assistance.